Mario R. Capecchi Ph.D.
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2007
Nobel prize also awarded to Sir Martin J. Evans and Oliver Smithies
National Medal of Science - Biological Sciences 2001
Molecular Geneticist. Introduced specific gene modifications in mice by using embryonic stem cells. Gene Targeting, Homeobox Genes, Development, Behavior.
Mother incarcerated as political prisoner, Germany. "At age 4½, I set off on my own, living in streets, orphanages; joining gangs of homeless children; generally hungry. Vivid recollections, brutal beyond description."
Patents
| Publication: | 1/16 |
| Publication No: | US 4,687,737 A |
| Title: | Mammalian suppressor genes |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | Aug. 18, 1987 |
| Filing Date: | July 02, 1985 |
| Inventors: | Phillip A. Sharp, Newton, Massachusetts (US); Mario R. Capecchi, Salt Lake City, Utah (US); Uttam L. Raj Bhandary, Lexington, Massachusetts (US); and Frank A. Laski, Southfield, Michigan (US) |
| Assignee: | Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts |
| Abstract: | A method of suppressing a nonsense codon in a gene in a mammalian cell by preparing an oligonucleotide primer having a mismatched anticodon region corresponding to the nonsense codon; preparing a DNA template for production of a tRNA molecule enabling the insertion of an amino acid when the nonsense codon is translated; forming a suppressor gene from said template and primer by site specific mutagenesis; and transforming the suppressor gene into the cell. |
| Representative Figure: | 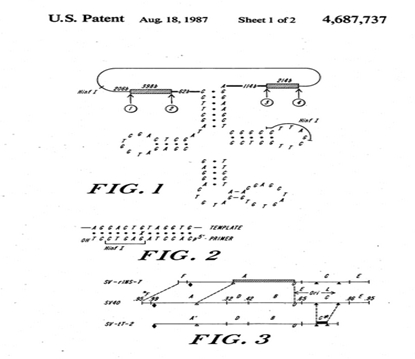 |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 2/16 |
| Publication No: | US 5,464,764 A |
| Title: | Positive-negative selection methods and vectors |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | Nov 07, 1995 |
| Filing Date: | Feb. 04, 1993 |
| Inventors: | Mario R. Capecchi, Salt Lake City, Utah (US); and Kirk R. Thomas, Salt Lake City, Utah (US) |
| Assignee: | University of Utah Research Foundation, Salt Lake City, Utah |
| Abstract: | Positive-negative selector (PNS) vectors are provided for modifying a target DNA sequence contained in the genome of a target cell capable of homologous recombination. The vector comprises a first DNA sequence which contains at least one sequence portion which is substantially homologous to a portion of a first region of a target DNA sequence. The vector also includes a second DNA sequence containing at least one sequence portion which is substantially homologous to another portion of a second region of a target DNA sequence. A third DNA sequence is positioned between the first and second DNA sequences and encodes a positive selection marker which when expressed is functional in the target cell in which the vector is used. A fourth DNA sequence encoding a negative selection marker, also functional in the target cell, is positioned 5' to the first or 3' to the second DNA sequence and is substantially incapable of homologous recombination with the target DNA sequence. The invention also includes transformed cells containing at least one predetermined modification of a target DNA sequence contained in the genome of the cell. In addition, the invention includes organisms such as non-human transgenic animals and plants which contain cells having predetermined modifications of a target DNA sequence in the genome of the organism. |
| Representative Figure: | |
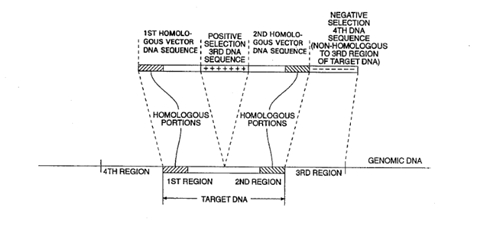 | |
| Family Members | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 3/16 |
| Publication No: | US 2004/0197317 A1 |
| Title: | Persistent expression of candidate molecule in proliferating stem and progenitor cells for delivery of therapeutic products |
| Publication Type: | Patent Application Publication |
| Publication Date: | Oct. 07, 2004 |
| Filing Date: | Feb. 27, 2004 |
| Inventors: | Mahendra S. Rao, Timonium MD (US); Mario R. Capecchi |
| Assignee: | |
| Abstract: | A method of obtaining and the resulting isolated progenitor or stem cell population of proliferating cells persistently expressing a candidate molecule. Further, novel methods of ex vivo gene product (e.g., protein) production and treating symptoms of neurological or neurodegenerative disorders are also provided. |
| Representative Figure: | None |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 4/16 |
| Publication No: | US2004/0197353 A1 |
| Title: | Population of hoxb8 mutants and uses in identifying agents for treating repetitive behaviors |
| Publication Type: | Patent Application Publication |
| Publication Date: | Oct. 07, 2004 |
| Filing Date: | May 21, 2004 |
| Inventors: | Joy M. Greer, Salt Lake City UT (US); Mario R. Capecchi |
| Assignee: | |
| Abstract: | This invention provides in vivo and in vitro methods of screening for an agent or a combination of agents that reduces one or more repetitive behaviors, comprising contacting neuronal cells of an animal with a HOXB8 gene mutation with the agent combination of agents to be screened, and determining whether one or more repetitive behaviors of the animal is reduced or whether one or more biochemical correlates of repetitive behaviors is reduced, the reduction in one or more repetitive behaviors or biochemical correlates indicating an agent or combination of agents that reduces repetitive behaviors. The invention also provides method of treating a subject with repetitive behaviors, comprising administering a therapeutically effective dose of the agent or combination of agents identified by the screening method. Further provided is a population of animals with a HOXB8 gene mutation, wherein more than 30% of the animals have excessive grooming behaviors and wherein less than 10% of the animals show skeletal defects. |
| Representative Figure: | None |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 5/16 |
| Publication No: | US 2005/0048041 A1 |
| Title: | Persistent expression of candidate molecule in proliferating stem and progenitor cells for delivery of therapeutic products |
| Publication Type: | Patent Application Publication |
| Publication Date: | Mar. 3, 2005 |
| Filing Date: | Jun. 15, 2004 |
| Inventors: | Mahendra S. Rao, Timonium MD (US); Mario R. Capecchi |
| Assignee: | |
| Abstract: | A method of obtaining and the resulting isolated progenitor or stem cell population of proliferating cells persistently expressing a candidate molecule. Further, novel methods of ex vivo gene product (e.g., protein) production and treating symptoms of neurological or neurodegenerative disorders are also provided. |
| Representative Figure: | None |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 6/16 |
| Publication No: | US 2005/0149998 A1 |
| Title: | Cells and non-human organisms containing predetermined genomic modifications and positive-negative selection methods and vectors for making same |
| Publication Type: | Patent Application Publication |
| Publication Date: | July 7, 2005 |
| Filing Date: | Dec. 23, 2003 |
| Inventors: | Mario R. Capecchi, Salt Lake City, UT (US); Kirk R. Thomas, Salt Lake City, UT (US) |
| Assignee: | |
| Abstract: | Positive-negative selector (PNS) vectors are provided for modifying a target DNA sequence contained in the genome of a target cell capable of homologous recombination. The vector comprises a first DNA sequence which contains at least one sequence portion which is substantially homologous to a portion of a first region of a target DNA sequence. The vector also includes a second DNA sequence containing at least one sequence portion which is substantially homologous to another portion of a second region of a target DNA sequence. A third DNA sequence is positioned between the first and second DNA sequences and encodes a positive selection marker which when expressed is functional in the target cell in which the vector is used. A fourth DNA sequence encoding a negative selection marker, also functional in the target cell, is positioned 5' to the first or 3' to the second DNA sequence and is substantially incapable of homologous recombination with the target DNA sequence. The invention also includes transformed cells containing at least one predetermined modification of a target DNA sequence contained in the genome of the cell. In addition, the invention includes organisms such as non-human transgenic animals and plants which contain cells having predetermined modifications of a target DNA sequence in the genome of the organism. |
| Representative Figure: | 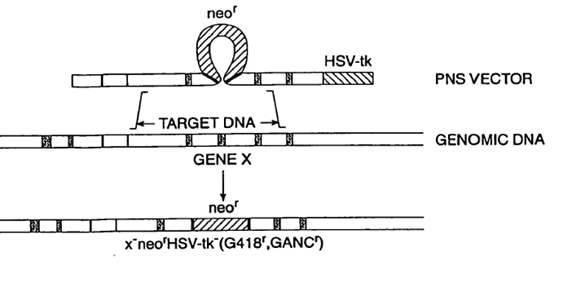 |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 7/16 |
| Publication No: | US 2008/0295192 A1 |
| Title: | SELF-INDUCED DELETION OF DNA |
| Publication Type: | Patent Application Publication |
| Publication Date: | Nov. 27, 2008 |
| Filing Date: | June 7, 2007 |
| Inventors: | Kirk R. Thomas, Kenneth E. Bernstein, Michaeline Bunting, Joy Greer, Mario Capecchi, |
| Assignee: | |
| Abstract: | The present invention is directed to a method for deleting DNA sequences in a tissue specific manner. In one embodiment, DNA sequences are specifically deleted in germline tissue. In a second embodiment, DNA sequences are specifically deleted in desired somatic tissue. The present invention is further directed to a nucleic acid molecule for use in the method. More specifically, a nucleic acid molecule is provide by the present invention which comprises (a) a recombinase site, (b) a tissue-specific promoter, (c) a recombinase gene, (d) a foreign DNA, and (e) a recombinase site. The nucleic acid molecule may further comprise a gene which is desired to be incorporated into and expressed in a transgenic organism. The method can be used in both plants and animals, and has many applications as described herein. |
| Representative Figure: | 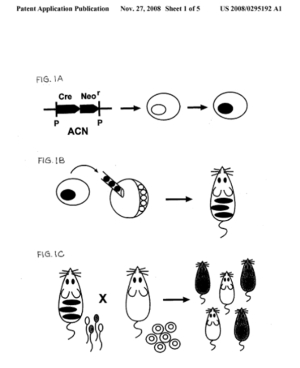 |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 8/16 |
| Publication No: | US 5,487,992 A |
| Title: | Cells And Non-human Organisms Containing Predetermined Genomic Modifications And Positive-negative Selection Methods And Vectors For Making Same |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | Jan. 30, 1996 |
| Filing Date: | June 28, 1993 |
| Inventors: | Mario R. Capecchi; Kirk R. Thomas |
| Assignee: | University of Utah Research Foundation |
| Abstract: | Positive-negative selector (PNS) vectors are provided for modifying a target DNA sequence contained in the genome of a target cell capable of homologous recombination. The vector comprises a first DNA sequence which contains at least one sequence portion which is substantially homologous to a portion of a first region of a target DNA sequence. The vector also includes a second DNA sequence containing at least one sequence portion which is substantially homologous to another portion of a second region of a target DNA sequence. A third DNA sequence is positioned between the first and second DNA sequences and encodes a positive selection marker which when expressed is functional in the target cell in which the vector is used. A fourth DNA sequence encoding a negative selection marker, also functional in the target cell, is positioned 5' to the first or 3' to the second DNA sequence and is substantially incapable of homologous recombination with the target DNA sequence. The invention also includes transformed cells containing at least one predetermined modification of a target DNA sequence contained in the genome of the cell. In addition, the invention includes organisms such as non-human transgenic animals and plants which contain cells having predetermined modifications of a target DNA sequence in the genome of the organism. |
| Representative Figure: | 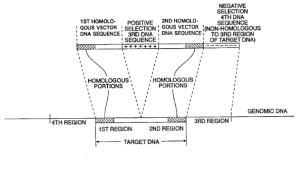 |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 9/16 |
| Publication No: | US 5627059 A |
| Title: | Cells and non-human organisms containing predetermined genomic modifications and positive-negative selection methods and vectors for making same |
| Publication Type: | Grant |
| Publication Date: | May 06, 1997 |
| Filing Date: | June 05, 1995 |
| Inventors: | Mario R. Capecchi; Kirk R. Thomas |
| University of Utah | |
| Abstract: | Positive-negative selector (PNS) vectors are provided for modifying a target DNA sequence contained in the genome of a target cell capable of homologous recombination. The vector comprises a first DNA sequence which contains at least one sequence portion which is substantially homologous to a portion of a first region of a target DNA sequence. The vector also includes a second DNA sequence containing at least one sequence portion which is substantially homologous to another portion of a second region of a target DNA sequence. A third DNA sequence is positioned between the first and second DNA sequences and encodes a positive selection marker which when expressed is functional in the target cell in which the vector is used. A fourth DNA sequence encoding a negative selection marker, also functional in the target cell, is positioned 5' to the first or 3' to the second DNA sequence and is substantially incapable of homologous recombination with the target DNA sequence. The invention also includes transformed cells containing at least one predetermined modification of a target DNA sequence contained in the genome of the cell. In addition, the invention includes organisms such as non-human transgenic animals and plants which contain cells having predetermined modifications of a target DNA sequence in the genome of the organism. |
| Representative Figure: | 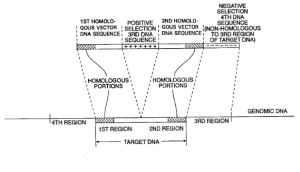 |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 10/16 |
| Publication No: | US 5,631,153 A |
| Title: | Cells and non-human organisms containing predetermined genomic modifications and positive-negative selection methods and vectors for making same |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | May 20, 1997 |
| Filing Date: | June 5, 1995 |
| Inventors: | Mario R. Capecchi; Kirk R. Thomas |
| Assignee: | University of Utah |
| Abstract: | Positive-negative selector (PNS) vectors are provided for modifying a target DNA sequence contained in the genome of a target cell capable of homologous recombination. The vector comprises a first DNA sequence which contains at least one sequence portion which is substantially homologous to a portion of a first region of a target DNA sequence. The vector also includes a second DNA sequence containing at least one sequence portion which is substantially homologous to another portion of a second region of a target DNA sequence. A third DNA sequence is positioned between the first and second DNA sequences and encodes a positive selection marker which when expressed is functional in the target cell in which the vector is used. A fourth DNA sequence encoding a negative selection marker, also functional in the target cell, is positioned 5' to the first or 3' to the second DNA sequence and is substantially incapable of homologous recombination with the target DNA sequence. The invention also includes transformed cells containing at least one predetermined modification of a target DNA sequence contained in the genome of the cell. In addition, the invention includes organisms such as non-human transgenic animals and plants which contain cells having predetermined modifications of a target DNA sequence in the genome of the organism. |
| Representative Figure: | 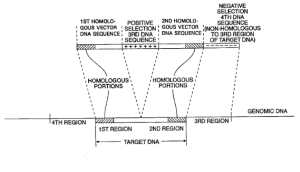 |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 11/16 |
| Publication No: | US 6,204,061 B1 |
| Title: | Cells and non-human organisms containing predetermined genomic modifications and positive-negative selection methods and vectors for making same |
| Publication Type: | Grant |
| Publication Date: | Mar. 20, 2001 |
| Filing Date: | Jan. 9, 1997 |
| Inventors: | Mario R. Capecchi; Kirk R. Thomas |
| Assignee: | University of Utah Research Foundation |
| Abstract: | Positive-negative selector (PNS) vectors are provided for modifying a target DNA sequence contained in the genome of a target cell capable of homologous recombination. The vector comprises a first DNA sequence which contains at least one sequence portion which is substantially homologous to a portion of a first region of a target DNA sequence. The vector also includes a second DNA sequence containing at least one sequence portion which is substantially homologous to another portion of a second region of a target DNA sequence. A third DNA sequence is positioned between the first and second DNA sequences and encodes a positive selection marker which when expressed is functional in the target cell in which the vector is used. A fourth DNA sequence encoding a negative selection marker, also functional in the target cell, is positioned 5' to the first or 3' to the second DNA sequence and is substantially incapable of homologous recombination with the target DNA sequence. The invention also includes transformed cells containing at least one predetermined modification of a target DNA sequence contained in the genome of the cell. In addition, the invention includes organisms such as non-human transgenic animals and plants which contain cells having predetermined modifications of a target DNA sequence in the genome of the organism. |
| Representative Figure: | 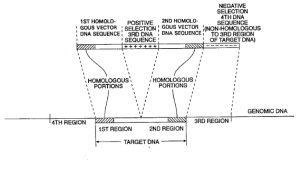 |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 12/16 |
| Publication No: | US 6,689,610 B1 |
| Title: | Cells and non-human organisms containing predetermined genomic modifications and positive-negative selection methods and vectors for making same |
| Publication Type: | Grant |
| Publication Date: | Feb. 10, 2004 |
| Filing Date: | Nov. 28, 1000 |
| Inventors: | Mario R. Capecchi; Kirk R. Thomas |
| Assignee: | University of Utah Research Foundation |
| Abstract: | Positive-negative selector (PNS) vectors are provided for modifying a target DNA sequence contained in the genome of a target cell capable of homologous recombination. The vector comprises a first DNA sequence which contains at least one sequence portion which is substantially homologous to a portion of a first region of a target DNA sequence. The vector also includes a second DNA sequence containing at least one sequence portion which is substantially homologous to another portion of a second region of a target DNA sequence. A third DNA sequence is positioned between the first and second DNA sequences and encodes a positive selection marker which when expressed is functional in the target cell in which the vector is used. A fourth DNA sequence encoding a negative selection marker, also functional in the target cell, is positioned 5' to the first or 3' to the second DNA sequence and is substantially incapable of homologous recombination with the target DNA sequence. The invention also includes transformed cells containing at least one predetermined modification of a target DNA sequence contained in the genome of the cell. In addition, the invention includes organisms such as non-human transgenic animals and plants which contain cells having predetermined modifications of a target DNA sequence in the genome of the organism. |
| Representative Figures: | 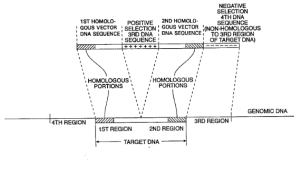 |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 13/16 |
| Publication No: | US 7,439,415 B2 |
| Title: | Population of hoxb8 mutants and uses in identifying agents for treating repetitive behaviors |
| Publication Type: | Grant |
| Publication Date: | Oct. 21, 2008 |
| Filing Date: | May 31, 2002 |
| Inventors: | Joy M. Greer, Mario R. Capecchi |
| Assignee: | |
| Abstract: | This invention provides in vivo and in vitro methods of screening for an agent or a combination of agents that reduces one or more repetitive behaviors, comprising contacting neuronal cells of an animal with a HOXB8 gene mutation with the agent combination of agents to be screened, and determining whether one or more repetitive behaviors of the animal is reduced or whether one or more biochemical correlates of repetitive behaviors is reduced, the reduction in one or more repetitive behaviors or biochemical correlates indicating an agent or combination of agents that reduces repetitive behaviors. The invention also provides method of treating a subject with repetitive behaviors, comprising administering a therapeutically effective dose of the agent or combination of agents identified by the screening method. Further provided is a population of animals with a HOXB8 gene mutation, wherein more than 30% of the animals have excessive grooming behaviors and wherein less than 10% of the animals show skeletal defects. |
| Representative Figure: | 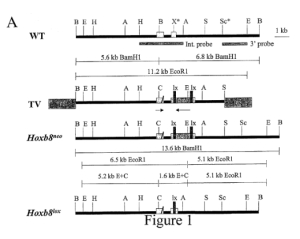 |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 14/16 |
| Publication No: | US 2010/0178696 A1 |
| Title: | IN VIVO GENOME-WIDE MUTAGENESIS |
| Publication Type: | Patent Application Publication |
| Publication Date: | July 15, 2010 |
| Filing Date: | Feb. 8, 2008 |
| Inventors: | Sen Wu; Mario R. Capecchi |
| Assignee: | University of Utah Research Foundation |
| Abstract: | Disclosed herein are compositions and methods for deleting or duplicating DNA in a mammalian genome. Also disclosed are compositions and methods for generating a random genome-wide chromosome rearrangement. Also disclosed are compositions and methods for streamlined construction of gene targeting vectors. |
| Representative Figure: |  |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 15/16 |
| Publication No: | US 2950166 A |
| Title: | Animal Model of Synovial Sarcoma |
| Publication Type: | Patent Application Publication |
| Publication Date: | Mar. 10, 2011 |
| Filing Date: | Jul. 22, 2008 |
| Inventors: | Malay Haldar; Mario R. Capecchi |
| Assignee: | University of Utah Research Foundation |
| Abstract: | Synovial sarcoma is an aggressive soft-tissue malignancy. Disclosed herein is an animal model of synovial sarcoma wherein one or more myogenic cells of the animal express recombinant SYT-SSX fusion polypeptide. Using this model, myoblasts were identified as a source of synovial sarcoma. Remarkably, within the skeletal muscle lineage, while expression of the oncoprotein in immature myoblasts leads to induction of synovial sarcoma with 100% penetrance, its expression in more differentiated cells induces myopathy without tumor induction. In addition, early widespread expression of the disclosed fusion protein disrupts normal embryogenesis, causing lethality. |
| Representative Figure: | 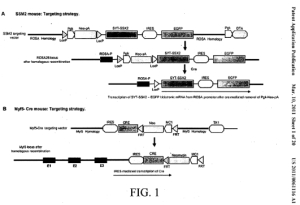 |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 16/16 |
| Publication No: | US 8,546,135 B2 |
| Title: | In vivo genome-wide mutagenesis |
| Publication Type: | Grant |
| Publication Date: | Oct. 1, 2013 |
| Filing Date: | Feb. 8, 2008 |
| Inventors: | Sen Wu; Mario R. Capecchi |
| Assignee: | University of Utah Research Foundation |
| Abstract: | Disclosed herein are compositions and methods for deleting or duplicating DNA in a mammalian genome. Also disclosed are compositions and methods for generating a random genome-wide chromosome rearrangement. Also disclosed are compositions and methods for streamlined construction of gene targeting vectors. |
| Representative Figure: | 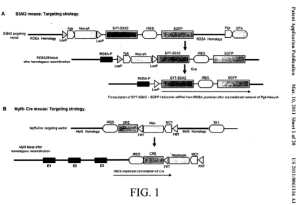 |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
Discover Your Abilities and Aspirations!
 $10 $25 $50 $100 Other
$10 $25 $50 $100 Other
Tax Exempt 501(c)3 Non-Profit Organization
Any Currency
“…the peace that is found in libraries and laboratories…” - Louis Pasteur
Copyright © 2023 Ganga Library Inc. All Rights reserved.;

Photo: © Nobel Foundation
Name: Mario Ramberg Capecchi Ph.D.
Birth: 6 October 1937, Verona, Italy
Institution: University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, Howard Hughes Medical Institute
Award: "for their discoveries of principles for introducing specific gene modifications in mice by the use of embryonic stem cells"
Subject: Genetics
Portion of cash: 1/2
National Medal of Science - Biological Sciences 2001
Biography
Publications
Patents
Quotations
Images
Mentor: James Watson
External Resources/Videos
Immigration