®
Virtual
Great • Alfred • Nobel • Gives • Aspiration!
Nobel & Laureates' Ideas & Thought Processes!
Sir Gregory Winter
Sir Gregory Winter
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2018
Co-nobelist: Frances H. Arnold, George P. Smith
“for the phage display of peptides and antibodies”
Patents
| Publication: | 1/19 |
| Publication No: | US 9657288 B2 |
| Title: | Connector compound peptide phage display peptides |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | May 23, 2017 |
| Filing Date: | August 22, 2013 |
| Inventors: | Gregory P. Winter, Christian Heinis |
| Original Assignee: | BicycleRD Ltd |
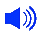
| Abstract: | The invention relates to a complex comprising a phage particle, said phage particle comprising (i) a polypeptide; (ii) a nucleic acid encoding the polypeptide of (i); (iii) a connector compound attached to said polypeptide wherein said connector compound is attached to the polypeptide by at least three discrete covalent bonds. The invention also relates to libraries, and to methods for making complexes and to methods of screening using same. |
| Representative Figure: | 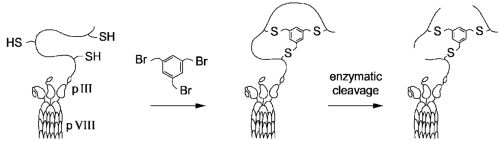 |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 2/19 |
| Publication No: | US 9629909 B2 |
| Title: | Methods for targeting pulmonary diseases with agents that bind a target in pulmonary tissue |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | April 25, 2017 |
| Filing Date: | March 6, 2013 |
| Inventors: | Rudolf M. T. de Wildt, Steve Holmes, Ian M. Tomlinson, Gregory P. Winter, Mary F. Fitzgerald, Justian Craig Fox, Armin Sepp, Jennifer Luckett, Benjamin P. Woolven |
| Original Assignee: | Domantis Ltd |
| Abstract: | Disclosed is the use of an agent (e.g., antibody fragment, antagonist, ligand, dAb monomer) that binds a target in pulmonary tissue for the manufacture of a long action or long therapeutic window formulation for local delivery to pulmonary tissue, and methods for administering an agent that binds a target in pulmonary tissue to a subject to produce a long therapeutic window in pulmonary tissue. The formulation is for, and the method comprises, administering locally to pulmonary tissue. Also disclosed is the use of antagonists of TNFR1 for the manufacture of a formulation or medicament for treating, preventing or suppressing lung inflammation or a respiratory disease, and methods of treating such diseases. Also disclosed are the use of agents a for the manufacture of a delivery device (e.g., inhaler, intranasal delivery device) for the treatment or prevention of lung inflammation or a respiratory disease, and a delivery device for the treatment or prevention of lung inflammation or a respiratory disease that contains an agent as described herein. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 3/13 |
| Publication No: | AU 2008201371 B2 |
| Title: | A process for recovering polypeptides that unfold reversibly from a polypeptide repertoire |
| Publication Type: | Australian Patent |
| Publication Date: | May 12, 2011 |
| Filing Date: | March 26, 2008 |
| Inventors: | Kristoffer H. J. Famm, Laurent S. Jespers, Philip C. Jones, Gregory P. Winter |
| Original Assignee: | Domantis Ltd |
| Abstract: | The invention relates to polypeptides that unfold reversibly (e.g., unfolds when heated and refolds when cooled), to repertoires containing polypeptides that unfold reversibly and to libraries that contain polypeptides that unfold reversibly or nucleic acids that encode polypeptides that unfold reversibly. The invention further relates to processes for producing a library enriched in polypeptides that unfold reversibly or nucleic acids encoding polypeptides that unfold reversibly, processes for selecting and/or isolating polypeptides that unfold reversibly, and to methods for producing a polypeptide that unfolds reversibly. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 4/19 |
| Publication No: | US 8338107 B2 |
| Title: | Method for producing polymers having a preselected activity |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | December 25, 2012 |
| Filing Date: | November 16, 2006 |
| Inventors: | William D. Huse, Gregory P. Winter, Lutz Riechmann, Joseph A. Sorge, Richard A. Lerner |
| Original Assignee: | Scripps Research Institute Medical Research Institute, Catalyst Assets LLC |
| Abstract: | The present invention relates to a method for isolating from the immunological gene repertoire a gene coding for a receptor having the ability to bind a preselected ligand. Receptors produced by the gene isolated by the method, particularly catalytic receptors, are also contemplated. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 5/19 |
| Publication No: | US 7858359 B2 |
| Title: | Method for tapping the immunological repertoire |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | December 28, 2010 |
| Filing Date: | November 9, 2006 |
| Inventors: | William D. Huse, Gregory P. Winter, Lutz Riechmann, Joseph A. Sorge, Richard A. Lerner |
| Original Assignee: | Medical Research Council, Stratagene California |
| Abstract: | The present invention relates to a method for isolating from the immunological gene repertoire a gene coding for a receptor having the ability to bind a preselected ligand. Receptors produced by the gene isolated by the method, particularly catalytic receptors, are also contemplated. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 6/19 |
| Publication No: | US 7189841 B2 |
| Title: | Method for tapping the immunological repertoire |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | March 13, 2007 |
| Filing Date: | August 2, 2004 |
| Inventors: | Richard A. Lerner, Joseph A. Sorge, Gregory P. Winter, Lutz Riechmann |
| Original Assignee: | UK Research and Innovation, Stratagene California, Scripps Research Institute |
| Abstract: | The present invention relates to a method for isolating from the immunological gene repertoire a gene coding for a receptor having the ability to bind a preselected ligand. Receptors produced by the gene isolated by the method, particularly catalytic receptors, are also contemplated. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 7/19 |
| Publication No: | CA 2525120 C |
| Title: | A process for recovering polypeptides that unfold reversibly from a polypeptide repertoire |
| Publication Type: | Canadian Patent |
| Publication Date: | April 30, 2013 |
| Filing Date: | May 14, 2004 |
| Inventors: | Laurent S. Jespers, Philip C. Jones, H. J. Kristoffer Famm, Gregory P. Winter |
| Original Assignee: | Domantis Ltd |
| Abstract: | The invention relates to polypeptides that unfold reversibly (e.g., unfolds when heated and refolds when cooled), to repertoires containing polypeptides that unfold reversibly and to libraries that contain polypeptides that unfold reversibly or nucleic acids that encode polypeptides that unfold reversibly. The invention further relates to processes for producing a library enriched in polypeptides that unfold reversibly or nucleic acids encoding polypeptides that unfold reversibly, processes for selecting and/or isolating polypeptides that unfold reversibly, and to methods for producing a polypeptide that unfolds reversibly. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 8/19 |
| Publication No: | US 6297004 B1 |
| Title: | Recombinant viruses displaying a nonviral polypeptide on their external surface |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | October 2, 2001 |
| Filing Date: | February 27, 1998 |
| Inventors: | Stephen J. Russell, Robert E. Hawkins, Gregory P. Winter |
| Original Assignee: | Biofocus Discovery Ltd |
| Abstract: | We have made retrovirus particles displaying a functional antibody fragment. We fused the gene encoding an antibody fragment directed against a hapten with that encoding the viral envelope protein (Pr80env) of the ecotropic Moloney murine leukemia virus. The fusion gene was co-expressed in ecotropic retroviral packaging cells with a retroviral plasmid carrying the neomycin phosphotransferase gene (neo), and retroviral particles with specific hapten biding activities were recovered. Furthermore the hapten-binding particles were able to transfer the neo gene and the antibody-envelope fusion gene to mouse fibroblasts. In principle, the display of antibody fragments on the surface of recombinant retroviral particles could be used to target virus to cells for gene delivery, or to retain the virus in target tissues, or for the construction of libraries of viral display packages. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 9/19 |
| Publication No: | US 6936464 B1 |
| Title: | Immune responses to fusion proteins |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | August 30, 2005 |
| Filing Date: | July 18, 1997 |
| Inventors: | Delin Zhu, Robert E Hawkins, Stephen J. Russell, Freda K. Stevenson, Gregory P Winter |
| Original Assignee: | Cancer Research Ventures Ltd, Cancer Research Technology Ltd |
| Abstract: | The invention relates to a nucleic acid construct for delivery into living cells in vivo for inducing an immune response in a patient to an idiotypic determinant present on a malignant B cell in the patient; the construct directing the expression of a fusion protein, said fusion protein comprising the idiotypic determinant and at least one T helper cell epitope from tetanus toxin. The invention further relates to a method of making the nucleic acid construct, a method of treating a patient, and to a composition comprising the nucleic acid construct. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 10/19 |
| Publication No: | US 5624821 A |
| Title: | Antibodies with altered effector functions |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | April 29, 1997 |
| Filing Date: | June 7, 1995 |
| Inventors: | Gregory P. Winter, Alexander R. Duncan, Dennis R. Burton |
| Original Assignee: | SB2 Inc |
| Abstract: | An antibody with an altered function, e.g. altered affinity for an effector ligand such as Fc receptor (FcR) on a cell or the C1 component of complement is produced by replacing at least one amino acid residue in the constant portion of the antibody with a different residue. |
| Representative Figure: | 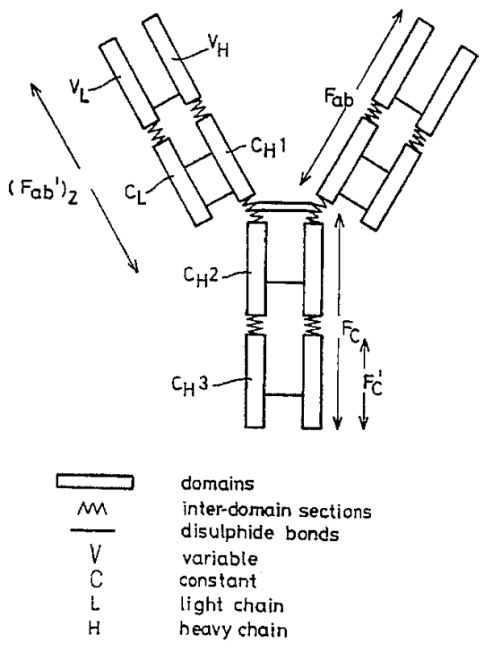 |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 11/19 |
| Publication No: | US 6569430 B1 |
| Title: | Antibodies to the antigen Campath-1 |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | May 27, 2003 |
| Filing Date: | March 21, 1995 |
| Inventors: | Herman Waldmann, Michael R. Clark, Gregory P. Winter, Lutz Riechmann |
| Original Assignee: | BTG International Ltd, UK Research and Innovation |
| Abstract: | An antibody is produced, which will bind effectively with the antigen Campath-1, and which has at least one complementarity determining region of rat origin, as identified in FIG. 2, which may be combined with a range of different foreign variable domain framework regions as desired, including framework regions of human origin. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 12/19 |
| Publication No: | CA 2130452 C |
| Title: | Altered antibodies, products and processes relating thereto |
| Publication Type: | Canadian Patent |
| Publication Date: | May 15, 2007 |
| Filing Date: | February 19, 1993 |
| Inventors: | Gregory P. Winter, Francis J. Carr, William J. Harris |
| Original Assignee: | SB2 Inc |
| Abstract: | The present invention relates to altered antibodies which are substantially immuno silent by virtue of their containing selected germ-line amino acid residues which replace one or more corresponding somatically mutated residues in a native antibody. In a process for making a gene for use in preparing such an antibody, one or more somatically mutated amino acid residues in a native antibody are identified as suitable candidate(s) for alteration. A nucleotide coding sequence is made which codes for selected germ-line amino acid residues to replace the one or more somatically mutated amino acid residues. The altered antibody can have variable (V) regions which comprise complementarity determining regions (CDRs) which provide the antibody with capacity to bind a specific antigen; and a selected and predominantly germ-line framework. In processes for making a gene for use in the preparation of such an antibody, there are the steps of (i) obtaining CDR encoding nucleotide sequences which encode CDRs with specificity for the specific antigen and (ii) combining these CDR encoding nucleotide sequences with framework encoding nucleotide sequences which encode the selected germ-line framework. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 13/19 |
| Publication No: | US 5565332 A |
| Title: | Production of chimeric antibodies - a combinatorial approach |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | October 15, 1996 |
| Filing Date: | September 23, 1992 |
| Inventors: | Hendricus R. J. M. Hoogenboom, Michael Baier, Laurent S. A. T. Jespers, Gregory P. Winter |
| Original Assignee: | Medical Research Council, MedImmune Ltd, ExxonMobil Chemical Patents Inc |
| Abstract: | Methods are disclosed which may be used for the production of antibodies, or antibody fragments, which have the same binding specificity as a parent antibody but which have increased human characteristics. Humanized antibodies may be obtained by chain shuffling, perhaps using phage display technology. In one embodiment, a polypeptide comprising a heavy or light chain variable domain of a non-human antibody specific for an antigen of interest is combined with a repertoire of human complementary (light or heavy) chain variable domains. Hybrid pairings which are specific for the antigen of interest are selected. Human chains from the selected pairings may then be combined with a repertoire of human complementary variable domains (heavy or light) and humanized antibody polypeptide dimers can then be selected for binding specificity for antigen. The methods may be combined with CDR-imprinting. In another embodiment, component part of an antigen-binding site of a no-human antibody known to bind a particular antigen is combined with a repertoire of component parts of an antigen-binding site of human antibody, forming a library of antibody polypeptide dimers with antigen-binding sites. Hybrids selected from this library may be used in a second humanizing shuffling step, or may already be of sufficient human character to be of value, perhaps after some modification to increase human character still further. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 14/19 |
| Publication No: | CA 2119930 C |
| Title: | Production of chimeric antibodies - a combinatorial approach |
| Publication Type: | Canadian Patent |
| Publication Date: | October 1, 2002 |
| Filing Date: | September 23, 1992 |
| Inventors: | Hendricus R. J. M. Hoogenboom, Michael Baier, Laurent S. A. T. Jespers, Gregory P. Winter |
| Original Assignee: | Medical Research Council, MedImmune Ltd |
| Abstract: | Methods are disclosed which may be used for the production of antibodies, or antibody fragments, which have the same binding specificity as a parent antibody but which have increased human characteristics. Humanised an-tibodies may be obtained by chain shuffling, perhaps using phage display technology. In one embodiment, a polypep-tide comprising a heavy or light chain variable domain of a non-human antibody specific for an antigen of interest is combined with a repertoire of human complementary (light or heavy) chain variable domains. Hybrid pairings which are specific for the antigen of interest are selected. Human chains from the selected pairings may then be combined with a repertoire of human complementary variable do-trains (heavy or light) and humanised antibody polypeptide dimers can then be selected for binding specificity for anti-gen. The methods may be combined with CDR-imprinting. In another embodiment, component part of an antigen-binding site of a non-human antibody known to bind a par-ticular antigen is combined with a repertoire of component parts of an antigen-binding site of human antibody, forming a library of antibody polypeptide dimers with antigen-bind-ing sites. Hybrids selected from this library may be used in a second humanising shuffling step, or may already be of suf-ficient human character to be of value, perhaps after some modification to increase human character still further. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 15/19 |
| Publication No: | US 6291161 B1 |
| Title: | Method for tapping the immunological repertiore |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | September 18, 2001 |
| Filing Date: | September 4, 1992 |
| Inventors: | Richard A. Lerner, Joseph A. Sorge, Gregory P. Winter, Lutz Riechmann |
| Original Assignee: | Richard A. Lerner, Joseph A. Sorge, Gregory P. Winter, Lutz Riechmann |
| Abstract: | The present invention relates to a method for isolating from the immunological gene repertoire a gene coding for a receptor having the ability to bind a preselected ligand. Receptors produced by the gene isolated by the method, particularly catalytic receptors, are also contemplated. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 16/19 |
| Publication No: | US 5830663 A |
| Title: | In situ recombinant PCR within single cells |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | November 3, 1998 |
| Filing Date: | August 10, 1992 |
| Inventors: | Michael J. Embleton, Guy Gorochov, Peter T. Jones, Gregory P. Winter |
| Original Assignee: | Medical Research Council |
| Abstract: | Disclosed is a method of treating a heterogeneous population of cells to link together copies of two or more nucleic acid sequences from at least some of the cells, the arrangement being such that copies of the DNA sequences from an individual cell are preferentially linked in the vicinity of the nucleic acid from which the copies are derived. Also disclosed are recombinant proteins expressed by the method of the invention and kits for performing said method. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 17/19 |
| Publication No: | CA 2109602 C |
| Title: | Methods for producing members of specific binding pairs |
| Publication Type: | Canadian Patent |
| Publication Date: | October 1, 2002 |
| Filing Date: | May 15, 1992 |
| Inventors: | Gregory P. Winter, Kevin S. Johnson, Andrew D. Griffiths, Andrew J. H. Smith |
| Original Assignee: | Medical Research Council, MedImmune Ltd |
| Abstract: | The invention provides methods and kits for producing specific binding pairs (sbp) members. Populations of polypeptide chain components of sbp members are combined to form libraries of sbps displayed by secreted replicable genetic display pack-ages (rgdp). At least one of the polypeptide chains is expressed as a fusion with a component of an rgdp which thereby displays that polypeptide chain at the surface of rgdp. At least one population of polypeptide chains is expressed from nucleic acid which is capable of being packaged using a component of an rgdp, whereby the genetic material of rgdps produced encodes a polypep-tide chain. The methods enable production of libraries of multimeric sbp members from a very large number of possible combina-tions. In one embodiment of the invention a method emplays "chain shuffling" in the production of sbp members of desired spe-cificity for a counterpart sbp member. Selection procedures are also described. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 18/19 |
| Publication No: | US 5225539 A |
| Title: | Recombinant altered antibodies and methods of making altered antibodies |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | July 6, 1993 |
| Filing Date: | October 25, 1991 |
| Inventors: | Gregory P. Winter |
| Original Assignee: | Medical Research Council |
| Abstract: | An altered antibody is produced by replacing the complementarity determining regions (CDRs) of a variable region of an immunoglobulin (Ig) with the CDRs from an Ig of different specificity, using recombinant DNA techniques. The gene coding sequences for producing the altered antibody may be produced by site-directed mutagenesis using long oligonucleotides |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 19/19 |
| Publication No: | CA 2086936 C |
| Title: | Method for producing members of specific binding pairs |
| Publication Type: | Canadian Patent |
| Publication Date: | August 16, 2005 |
| Filing Date: | July 10, 1991 |
| Inventors: | John Mccafferty, Anthony R. Pope, Kevin S. Johnson, Hendricus R. J. M. Hoogenboom, Andrew D. Griffiths, Ronald H. Jackson, Kaspar P. Holliger, James D. Marks, Timothy P. Clackson, David J. Chiswell, Gregory P. Winter, Timothy P. Bonnert |
| Original Assignee: | MedImmune Ltd, UK Research and Innovation |
| Abstract: | A member of a specific binding pair (sbp) is identified by expressing DNA encoding a genetically diverse population of such sbp members in recombinant host cells in which the sbp members are displayed in functional form at the surface of a secreted recombinant genetic display package (rgdp) containing DNA encoding the sbp member or a polypeptide component thereof, by virtue of the sbp member or a polypeptide component thereof being expressed as a fusion with a capsid component of the rgdp. The displayed sbps may be selected by affinity with a complementary sbp member, and the DNA recovered from selected rgdps for expression of the selected sbp members. Antibody sbp members may be thus obtained, with the different chains thereof expressed, one fused to the capsid component and the other in free form for association with the fusion partner polypeptide. A phagemid may be used as an expression vector, with said capsid fusion helping to package the phagemid DNA. Using this method libraries of DNA encoding respective chains of such multimeric sbp members may be combined, thereby obtaining a much greater generic diversity in the sbp members than could easily be obtained by conventional methods. |
| Representative Figure: |  |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
Discover Your Abilities and Aspirations!
 $10 $25 $50 $100 Other
$10 $25 $50 $100 Other
Tax Exempt 501(c)3 Non-Profit Organization
Any Currency
“One comes to be of just such stuff as that on which the mind is set” - Maithri Upanishath, VI.34:3
“…the peace that is found in libraries and laboratories…” - Louis Pasteur
“…the peace that is found in libraries and laboratories…” - Louis Pasteur
Contact Us E-Mail: info@GangaLib.org
Ganga library non-profit 501(c)(3) org. Contributions tax deductible. IRS Tax ID 46-2892728
Copyright © 2023 Ganga Library Inc. All Rights reserved.;
Copyright © 2023 Ganga Library Inc. All Rights reserved.;

Photo: Aga Machaj, Wiki
Name: Sir Gregory Paul Winter
Birth: 14 April 1951, Leicester, United Kingdom
Residence: MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Cambridge, United Kingdom
Award: "for the phage display of peptides and antibodies"
Portion of Cash: 1/3
Patents