Theodor Hansch Ph.D.
The Nobel Prize in Physics 2005
Co-nobelists: Roy J. Glauber, John L. Hall
Prize motivation: "for their contributions to the development of laser-based precision spectroscopy, including the optical frequency comb technique."
Patents
| Publication: | 1/12 |
| Publication No: | US7672342 B2 |
| Title: | Method and radiation source for generating pulsed coherent radiation |
| Publication Type: | Grant |
| Publication Date: | March 2, 2010 |
| Filing Date: | May 24, 2005 |
| Inventors: | Christoph Gohle, Theodor W. Hänsch, Ronald Holzwarth, Thomas Udem |
| Original Assignee: | MAX-PLANCK-Gesellschaft zur Förderung der Wissenschaften e.V. |
| Abstract: | A method of generating pulsed coherent radiation, comprises the step of generating high harmonic pulses by an interaction of laser light pulses with a non-linear medium contained in a resonant cavity, wherein the non-linear medium is arranged in an environment of reduced pressure. Furthermore, a radiation source of generating pulsed coherent radiation is described, comprising a laser pulse source for generating laser light pulses, a resonant cavity including a non-linear medium for generating high harmonic pulses by an interaction of the laser light pulses with the non-linear medium, wherein the non-linear medium is arranged in an environment of reduced pressure. |
Representative Figure: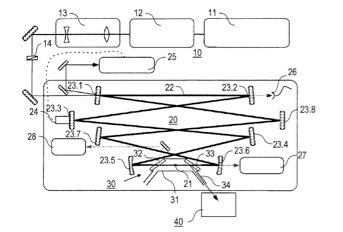 | |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO |
| Publication: | 2/12 |
| Publication No: | US7026594 B2 |
| Title: | Method and device for producing radio frequency waves |
| Publication Type: | Grant |
| Publication Date: | April 11, 2006 |
| Filing Date: | September 5, 2001 |
| Inventors: | Ronald Holzwarth, Thomas Udem, Theodor Hansch |
| Original Assignee: | Max-Planck-Gesellschaft Zur Forderung Der Wissenschaft E.V. |
| Abstract: | The invention relates to a method for producing radio frequency waves, whereby a pulse laser for producing light pulses having a predetermined spectrum of frequency modes and a predetermined recurrence frequency is operated. The light pulses of the pulse laser are detected by means of a detector device, and corresponding electrical output signals forming the radio frequency signals are produced. Said pulse laser is actuated in a stabilized manner by means of an optical reference signal in such a way that the recurrence frequency of the light pulse is fixed. The invention also relates to a radio frequency generator for implementing said method. |
Representative Figure: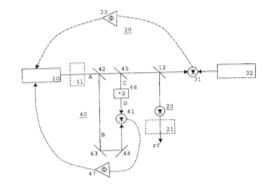 | |
| Family Members | DE10044405A1, DE10044405C2, US20040021056, WO2002021647A1 |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO |
| Publication: | 3/12 |
| Publication No: | US6785303 B1 |
| Title: | Generation of stabilized, ultra-short light pulses and the use thereof for synthesizing optical frequencies |
| Publication Type: | Grant |
| Publication Date: | August 31, 2004 |
| Filing Date: | March 10, 2000 |
| Inventors: | Ronald Holzwarth, Jörg Reichert, Thomas Udem, Theodor W. Hänsch |
| Original Assignee: | Max-Planck-Gesellschaft Zur Forderung Der Wissenschaften E. V. |
| Abstract: | A process for operation of a laser device (1) is described, whereby circulating light pulses each comprising spectral components according to a plurality of longitudinal modes of a resonator configuration (3) are generated in the resonator configuration (3) and subjected to a compensation of group velocity dispersion, and a predetermined linear dispersion is introduced into the light path of the resonator configuration (3), so that at least one mode has a predetermined frequency and/or the mode distance between the modes has a predetermined value. Furthermore, regulations for stabilizing the laser device on the basis of this process and applications of the regulations for the generation for stabilized, ultra-short light pulses, generation of optical frequencies and in the frequency and/or time measuring technique as well as in the spectroscopy are described. |
Representative Figure: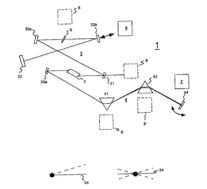 | |
| Family Members | DE19911103A1, DE19911103B4, EP1161782A1, EP1161782B1, WO2000055948A1 |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO |
| Publication: | 4/12 |
| Publication No: | US6724788 B1 |
| Title: | Method and device for generating radiation with stabilized frequency |
| Publication Type: | Grant |
| Publication Date: | April 20, 2004 |
| Filing Date: | September 6, 2000 |
| Inventors: | Ronald Holzwarth, Theodor W. Hänsch, Thomas Udem |
| Original Assignee: | Max-Planck-Gesellschaft Zur Forderung Der Wissenschaften E.V. |
| Abstract: | A method for generating radiation with stabilized frequency, comprises the steps of providing laser light pulses with a repetition frequency fR, said pulses comprising a plurality of N frequency components fn with fn=n fR+f0, wherein f0 represents an offset frequency with n=1 , . . . , N, said frequency components forming a comb with first and second different frequency portions, and generating a primary light output with at least one output frequency component corresponding to the difference of frequencies of said first and second frequency portions. |
Representative Figure: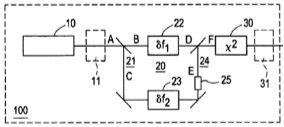 | |
| Family Members | WO2002021649A2, WO2002021649A3 |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO, USPTO Assignment |
| Publication: | 5/12 |
| Publication No: | US6476383 B1 |
| Title: | Device and method for generating and manipulating coherent matter waves |
| Publication Type: | Grant |
| Publication Date: | November 5, 2002 |
| Filing Date: | August 31, 1999 |
| Inventors: | Tilman Esslinger, Theodor W. Hänsch, Immanuel Bloch |
| Original Assignee: | Max-Planck-Gesellschaft Zur Forderung Der Wissenschaften E.V. |
| Abstract: | A device for generating and manpulating coherent matter waves contains a magnetic trap being adapted to form a magnetic trapping potential for gas atoms, said magnetic trap comprising a plurality of trap coils being connected with a current supply device and including two quadrupole coils and one Ioffe coil, wherein the trap coils are arranged in such a relative position that a common trap is formed, said common trap having a quadrupole trap shape with one trap minimum if the quadrupole coils are in an operation condition and the Ioffe coil is in a currentless condition or two trap minima or a Ioffe trap shape if all the quadrupole and Ioffe coils are in an operation condition and a shielding device protecting the magnetic trap against external magnetic fields. A method of continuous extracting matter waves from the trap is described. |
Representative Figure: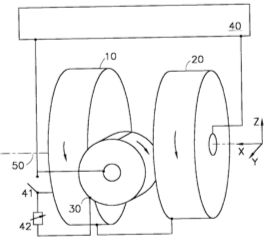 | |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO |
| Publication: | 6/12 |
| Publication No: | US6038055 A |
| Title: | Method and device for generating phase-coherent light pulses |
| Publication Type: | Grant |
| Publication Date: | March 14, 2000 |
| Filing Date: | November 12, 1998 |
| Inventors: | Theodor Hansch, Tilman Heupel, Martin Weitz |
| Original Assignee: | Max-Planck-Gesellschaft Zur Forderung Der Wissenschaften E.V. |
| Abstract: | For the generation of amplified, phase-coherent light pulses, a sequence of phase-coherent, equidistant input light pulses (21) is coupled into a resonator device (1) with at least two resonator mirrors (11, 14), forming a light path (10) with a predetermined resonator length, in such a way that the coupled in input light pulses in the resonator device are linearly superimposed in succession to form at least one circulating light pulse, whereby the circulating light pulse is coupled out of the resonator device as an output light pulse (31) as soon as the circulating light pulse has reached a preset minimum level of energy. |
Representative Figure: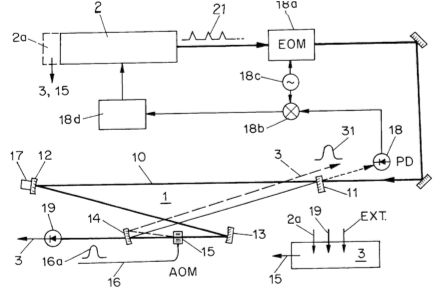 | |
| Family Members | DE19750320C1 |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO |
| Publication: | 7/12 |
| Publication No: | US5079444 A |
| Title: | Method and apparatus for producing a nonlinear interaction between two electromagnetic waves |
| Publication Type: | Grant |
| Publication Date: | January 7, 1992 |
| Filing Date: | February 27, 1990 |
| Inventors: | Reinald Kallenbach, Claus Zimmermann, Dieter Meschede, Theodor Hansch |
| Original Assignee: | Max-Planck-Gesellschaft Zur Foerderung Der Wissenschaften E.V. |
| Abstract: | Method and apparatus for producing a non-linear interaction between two electromagnetic waves, e.g. a laser beam and a microwave beam, in a non-linear optical medium, wherein one wave passes through a predetermined region of the medium in a zig-zag path, and the other traverses the predetermined region of the non-linear medium in two opposed directions in such a manner that an interaction-production phase-matching of the two waves is obtained not only in the departing but also in the approaching segments of the zig-zag path. |
Representative Figure: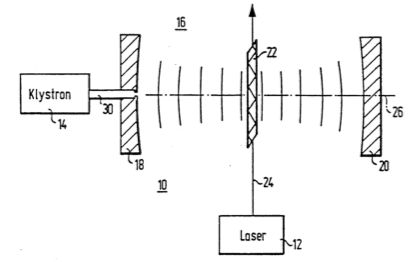 | |
| Family Members | DE3906068A1, DE3906068C2 |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO |
| Publication: | 8/12 |
| Publication No: | US4700150 A |
| Title: | External laser frequency stabilizer |
| Publication Type: | Grant |
| Publication Date: | October 13, 1987 |
| Filing Date: | une 14, 1985 |
| Inventors: | John L. Hall, Theodor W. Hansch |
| Original Assignee: | Stanford University |
| Abstract: | An external laser frequency stabilizer combines an acousto-optic frequency shifter and a fast electro-optic phase modulator. A compensating electronic delay line in a crossover network provides a near-ideal transducer response while keeping the voltage across the electro-optic crystal away from the amplifier limits. |
Representative Figure: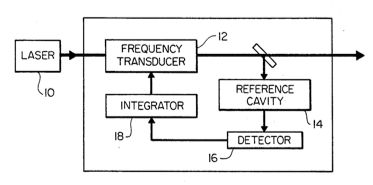 | |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO, USPTO Assignment |
| Publication: | 9/12 |
| Publication No: | US4451923 A |
| Title: | Method of an apparatus for measuring optical frequency variations |
| Publication Type: | Grant |
| Publication Date: | May 29, 1984 |
| Filing Date: | December 1, 1980 |
| Inventors: | Theodor W. Hansch, Bernard J. Couillaud |
| Original Assignee: | Hansch Theodor W, Couillaud Bernard J |
| Abstract: | Herein is disclosed a method of and apparatus for measuring optical frequency variations wherein linearly-polarized incident light generated by a tunable laser or the like is delivered to a passive resonant cavity incorporating a linear polarizer such as a Brewster plate so that the reflected light acquires a frequency-dependent elliptical polarization which can be detected by a simple polarization analyzer providing a signal correlated with the frequency variation of the laser. Such signal can be utilized as a feedback error signal to stabilize the laser frequency, or to adjust the cavity resonance. If the cavity is tunable, tuning thereof will in turn provide a precision method for tuning of the laser itself. |
Representative Figure: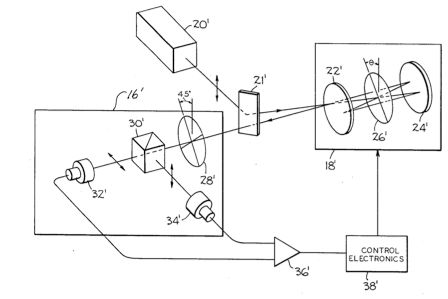 | |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO |
| Publication: | 10/12 |
| Publication No: | US4191473 A |
| Title: | Method of and apparatus for measuring the absolute wavelength of a source of unknown frequency radiation |
| Publication Type: | Grant |
| Publication Date: | March 4, 1980 |
| Filing Date: | January 9, 1978 |
| Inventors: | Theodor W. Hansch |
| Original Assignee: | Theodor W. Hansch |
| Abstract: | The invention constitutes a method of and apparatus for measuring the absolute wavelength of a source of unknown frequency radiation through directing radiant energy of known frequency against a diffraction grating of predetermined pattern so as to image a calibrated scale on a suitable screen or the like, and then directing the radiant energy from the unknown frequency source along the same path to the diffraction grating and onto the screen, where a visually available easy-to-read measurement of the wavelength appears. |
Representative Figure: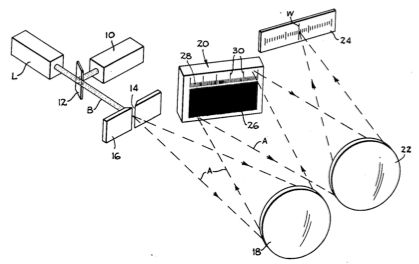 | |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO |
| Publication: | 11/12 |
| Publication No: | US3781700 A |
| Title: | Optical element system and method for amplifying image forming light rays |
| Publication Type: | Grant |
| Publication Date: | December 25, 1973 |
| Filing Date: | February 11, 1971 |
| Inventors: | Theodor W. Hansch, Frank L. Varsanyi |
| Original Assignee: | Univ Leland Stanford Junior |
| Abstract: | An optical element system and method for amplifying light rays such that a typical plane in object space can be transferred and amplified as an image on a screen and image space using an organic dye media disposed in the path of the amplifying rays and excited by light pulses of having predetermined characteristics. Uses suggest themselves in widely varying field of infrared, ultraviolet and visible optical instruments and computers and other devices. |
Representative Figure: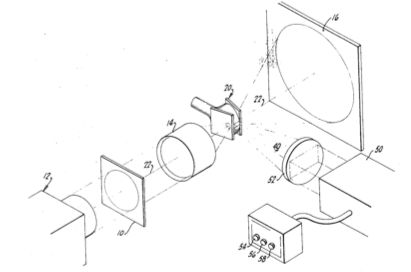 | |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO |
| Publication: | 12/12 |
| Publication No: | US2011/0267625 A1 |
| Title: | Interferometer with frequency combs and synchronization scheme |
| Publication Type: | Application |
| Publication Date: | November 3, 2011 |
| Filing Date: | July 20, 2009 |
| Inventors: | Guy Guelachvili, Theodor W. Hänsch, Nathalie Picqué |
| Original Assignee: | Centre National De La Recherche Scientifique-Cnrs |
| Abstract: | An embodiment relates to an interferometer comprising: a first frequency comb; a second frequency comb adapted to interact with the first frequency comb in order to produce interferences; means for isolating the beating signal between a subset of frequency components among the frequency components of the two combs. This subset of frequency components may be preferably, but not necessarily, a single line of the first frequency comb and a single line of the second frequency comb; means for monitoring this beating signal and using it as a trigger or as a clock for the acquisition unit device recording the beating interference signal between the entire frequency components of the first and the second frequency combs. |
Representative Figure: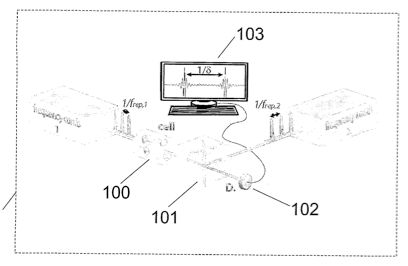 | |
| Family Members | CA2731301A1, CA2731303A1, CN102159926A, CN102159926B, CN102246016A, EP2310816A1, EP2310817A2, US20110261363, WO2010010437A1, WO2010010437A8, WO2010010438A2, WO2010010438A3, WO2010010438A8, WO2010010444A1 |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO, USPTO Assignment |
Discover Your Abilities and Aspirations!
 $10 $25 $50 $100 Other
$10 $25 $50 $100 Other
Tax Exempt 501(c)3 Non-Profit Organization
Any Currency
“…the peace that is found in libraries and laboratories…” - Louis Pasteur
Copyright © 2023 Ganga Library Inc. All Rights reserved.;

Photo Markus Possel, Wiki.
Name: Theodor W. Hänsch
Birth: 30 October 1941, Heidelberg, Germany
Institution: Max-Planck-Institut für Quantenoptik, Garching, Germany, Ludwig-Maximilians- Universität, Munich, Germany
Award: "for their contributions to the development of laser-based precision spectroscopy, including the optical frequency comb technique."
Subject: crystallography, electromagnetism
Portion of Cash: 1/3
Patents