®
Virtual
Great • Alfred • Nobel • Gives • Aspiration!
Nobel & Laureates' Ideas & Thought Processes!
Frances H. Arnold, Ph.D
Frances H. Arnold, Ph.D
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2018
Nobel co-recipients George P. Smith, Sir Gregory P. Winter
"for the directed evolution of enzymes"
Patents
| Publication: | 1/34 |
| Publication No: | US 10934531 B2 |
| Title: | Method for enantioselective carbene C—H insertion using an iron-containing protein catalyst |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | March 2, 2021 |
| Filing Date: | January 24, 2019 |
| Inventors: | Ruijie Zhang, Lena Wohlschlager, Hans H. Renata, Frances H. Arnold, Kai Chen |
| Assignee: | California Institute of Technology CalTech |
| Abstract: | Methods for catalyzing C—H insertion reactions using heme enzymes are described. The present disclosure provides a method for producing a C—H insertion product comprising providing an substrate having an sp3-hybridized C—H bond, a carbene precursor such as a diazo reagent, and a heme enzyme, and admixing the components in a reaction for a time sufficient to produce the C—H insertion product. Heme enzyme variants useful for carrying out in vivo and in vitro C—H insertion reactions, as well as expression vectors and host cells expressing the heme enzymes, are also described. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 2/34 |
| Publication No: | US 11008596 B2 |
| Title: | Cytochrome P450 BM3 enzyme variants for preparation of cyclopropanes |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | May 18, 2021 |
| Filing Date: | January 11, 2019 |
| Inventors: | Pedro S. Coelho, Eric M. Brustad, Frances H. Arnold, Zhan Wang, Jared C. Lewis |
| Assignee: | California Institute of Technology CalTech |
| Abstract: | The present invention provides methods for catalyzing the conversion of an olefin to any compound containing one or more cyclopropane functional groups using heme enzymes. In certain aspects, the present invention provides a method for producing a cyclopropanation product comprising providing an olefinic substrate, a diazo reagent, and a heme enzyme; and admixing the components in a reaction for a time sufficient to produce a cyclopropanation product. In other aspects, the present invention provides heme enzymes including variants and fragments thereof that are capable of carrying out in vivo and in vitro olefin cyclopropanation reactions. Expression vectors and host cells expressing the heme enzymes are also provided by the present invention. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 3/34 |
| Publication No: | US 10927355 B2 |
| Title: | Method for producing an organosilicon product |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | September 5, 2018 |
| Filing Date: | February 2, 2016 |
| Inventors: | ek Bik Jennifer Kan, Russell D. Lewis, Kai Chen, Frances H. Arnold |
| Assignee: | California Institute of Technology CalTech |
| Abstract: | The present invention provides compositions and methods for catalyzing the formation of carbon-silicon bonds using heme proteins. In certain aspects, the present invention provides heme proteins, including variants and fragments thereof, that are capable of carrying out in vitro and in vivo carbene insertion reactions for the formation of carbon-silicon bonds. In other aspects, the present invention provides methods for producing an organosilicon product, the method comprising providing a silicon-containing reagent, a carbene precursor, and a heme protein; and combining the components under conditions sufficient to produce an organosilicon product. Host cells expressing the heme proteins are also provided by the present invention. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 4/34 |
| Publication No: | US 10501762 B2 |
| Title: | Methods and systems for sulfimidation or sulfoximidation of organic molecules |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | December 10, 2019 |
| Filing Date: | July 12, 2016 |
| Inventors: | Christopher C. Farwell, John A. McIntosh, Frances H. Arnold |
| Assignee: | California Institute of Technology CalTech |
| Abstract: | The disclosure generally relates to the fields of synthetic organic chemistry. In particular, the present disclosure relates to methods and systems for the imidation of sulfides. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 5/34 |
| Publication No: | US 9708633 B2 |
| Title: | Stable, functional chimeric cellobiohydrolase class I enzymes |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | July 18, 2017 |
| Filing Date: | March 11, 2016 |
| Inventors: | Frances H. Arnold, Pete Heinzelman |
| Assignee: | California Institute of Technology CalTech |
| Abstract: | The present disclosure relates to CBH I chimera fusion polypeptides, nucleic acids encoding the polypeptides, and host cells for producing the polypeptides. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 6/34 |
| Publication No: | US 9334544 B2 |
| Title: | Cellulase compositions having improved thermostability and synergy |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | May 10, 2016 |
| Filing Date: | October 16, 2014 |
| Inventors: | Devin L. Trudeau, Frances H. Arnold, Toni M. Lee, Stephen L. Mayo |
| Assignee: | California Institute of Technology CalTech |
| Abstract: | A variant Cel5a endoglucanase has increased thermostability, increased enzymatic activity and/or increased expression in a host, relative to wild type Cel5a. The improved variant Cel5a endoglucanase may be used to hydrolyze more cellulose at a higher temperature for a more efficient and cost-effective production of biofuels as compared to wild type Cel5a. A variant Cel5a endoglucanase is combined with variant Cel6a and variant Cel7a cellobiohydrolases resulting in more effective hydrolysis of cellulose. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 7/34 |
| Publication No: | US 9145549 B2 |
| Title: | Regio- and enantioselective alkane hydroxylation with modified cytochrome P450 |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | September 29, 2015 |
| Filing Date: | June 2, 2014 |
| Inventors: | Frances H. Arnold, Matthew W. Peters, Peter Meinhold |
| Assignee: | California Institute of Technology CalTech |
| Abstract: | Cytochrome P450 BM-3 from Bacillus megaterium was engineered using a combination of directed evolution and site-directed mutagenesis to hydroxylate linear alkanes regio- and enantioselectively using atmospheric dioxygen as an oxidant. Mutant 9-10A-A328V hydroxylates octane primarily at the 2-position to form S-2-octanol (40% ee). Another mutant, 1-12G, hydroxylates alkanes larger than hexane primarily at the 2-position, but forms R-2-alcohols (40-55% ee). These biocatalysts are highly active for alkane substrates and support thousands of product turnovers. These regio- and enantio-selectivities are retained in whole-cell biotransformations with E. coli, where the engineered P450s can be expressed at high levels and the expensive cofactor is supplied endogenously. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 8/34 |
| Publication No: | US 9322001 B2 |
| Title: | Cytochrome P450 oxygenases |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | April 26, 2016 |
| Filing Date: | May 10, 2014 |
| Inventors: | Edgardo Farinas, Frances H. Arnold, Ulrich Schwaneberg, Anton Glieder |
| Assignee: | California Institute of Technology CalTech |
| Abstract: | Nucleic acids encoding cytochrome P450 variants are provided. The cytochrome P450 variants of have a higher alkane-oxidation capability, alkene-oxidation capability, and/or a higher organic-solvent resistance than the corresponding wild-type or parent cytochrome P450 enzyme. A preferred wild-type cytochrome P450 is cytochrome P450 BM-3. Preferred cytochrome P450 variants include those having an improved capability to hydroxylate alkanes and epoxidate alkenes comprising less than 8 carbons, and have amino acid substitutions corresponding to V78A, H236Q, and E252G of cytochrome P450 BM-3. Preferred cytochrome P450 variants also include those having an improved hydroxylation activity in solutions comprising co-solvents such as DMSO and THF, and have amino acid substitutions corresponding to T235A, R471A, E494K, and S1024E of cytochrome P450 BM-3. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 9/34 |
| Publication No: | US 9334517 B2 |
| Title: | Endoglucanase having enhanced thermostability and activity |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | May 10, 2016 |
| Filing Date: | April 7, 2014 |
| Inventors: | Toni M. Lee, Stephen L. Mayo, Frances H. Arnold, Devin Trudeau |
| Assignee: | California Institute of Technology CalTech |
| Abstract: | A variant Cel5a endoglucanase has increased thermostability, increased enzymatic activity and/or increased expression in a host, relative to wild type Cel5a. The improved variant Cel5a endoglucanase may be used to hydrolyze more cellulose at a higher temperature for a more efficient and cost-effective production of biofuels as compared to wild type Cel5a. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 10/34 |
| Publication No: | US 9322007 B2 |
| Title: | Stable fungal Cel6 enzyme variants |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | April 26, 2016 |
| Filing Date: | July 20, 2012 |
| Inventors: | Frances H. Arnold, Indira Wu |
| Assignee: | California Institute of Technology CalTech |
| Abstract: | The disclosure provides variant Cel6a enzymes having increased thermostability, methods of making and using such polypeptides. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 11/34 |
| Publication No: | US 9249401 B2 |
| Title: | Polypeptides having cellulase activity |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | February 2, 2016 |
| Filing Date: | April 6, 2010 |
| Inventors: | Frances H. Arnold, Pete Heinzelman |
| Assignee: | California Institute of Technology CalTech |
| Abstract: | The present disclosure relates to CBH II chimera fusion polypeptides, nucleic acids encoding the polypeptides, and host cells for producing the polypeptides. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 12/34 |
| Publication No: | US 8252559 B2 |
| Title: | Methods and systems for selective fluorination of organic molecules |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | August 28, 2012 |
| Filing Date: | February 4, 2009 |
| Inventors: | Rudi Fasan, Frances H. Arnold |
| Assignee: | California Institute of Technology CalTech |
| Abstract: | A method and system for selectively fluorinating organic molecules on a target site wherein the target site is activated and then fluorinated are shown together with a method and system for identifying a molecule having a biological activity.y. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 13/34 |
| Publication No: | US 7704715 B2 |
| Title: | Peroxide-driven cytochrome P450 oxygenase variants |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | April 27, 2010 |
| Filing Date: | October 11, 2008 |
| Inventors: | Patrick C. Cirino, Frances H. Arnold |
| Assignee: | California Institute of Technology CalTech |
| Abstract: | The invention relates to novel variants of cytochrome P450 oxygenases. These variants have an improved ability to use peroxide as an oxygen donor as compared to the corresponding wild-type enzyme. These variants also have an improved thermostability as compared to the cytochrome P450 BM-3 F87A mutant. Preferred variants include cytochrome P450 BM-3 heme domain mutants having I58V, F87A, H100R, F107L, A135S, M145A/V, N239H, S274T, L324I, I366V, K434E, E442K, and/or V446I amino acid substitutions. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 14/34 | |
| Publication No: | US 8802401 B2 | |
| Title: | Methods and compositions for preparation of selectively protected carbohydrates | |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent | |
| Publication Date: | August 12, 2014 | |
| Filing Date: | June 18, 2008 | |
| Inventors: | Frances H. Arnold, Chi-Huey Wong, Yuuichi Mitsuda, Michael M. Chen, Clay Bennett, William Greenberg, Jared Crawford Lewis, Sabine Bastian | |
| Assignee: | California Institute of Technology CalTech | |
| Abstract: | The disclosure relates to engineered P450 polypeptides and use of such polypeptides in chemoenzymatic methods to construct selectively protected carbohydrates, which are useful as building blocks for preparation of carbohydrate derivatives and oligosaccharides. | |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure | |
| Family | ||
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 15/34 |
| Publication No: | US 8026085 B2 |
| Title: | Methods and systems for selective fluorination of organic molecules |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | September 27, 2011 |
| Filing Date: | August 4, 2007 |
| Inventors: | Rudi Fasan, Frances H. Arnold |
| Assignee: | California Institute of Technology CalTech |
| Abstract: | A method and system for selectively fluorinating organic molecules on a target site wherein the target site is activated and then fluorinated are shown together with a method and system for identifying a molecule having a biological activity. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 16/34 | |
| Publication No: | US 7435570 B2 | |
| Title: | Thermostable peroxide-driven cytochrome P450 oxygenase variants and methods of use | |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent | |
| Publication Date: | October 14, 2008 | |
| Filing Date: | August 11, 2004 | |
| Inventors: | Frances H. Arnold, Patrick C. Cirino | |
| Assignee: | California Institute of Technology CalTech | |
| Abstract: | The invention relates to novel variants of cytochrome P450 oxygenases. These variants have at least one mutation improving their ability to use peroxide as an oxygen donor as compared to the corresponding wild-type enzyme. The variants also have at least one mutation improving thermostability as compared to the parent enzyme or corresponding wild-type enzyme. Preferred variants include cytochrome P450 BM-3 heme domain variants having L52I, I58V, F87A, H100R, S106R, F107L, A135S, M145A/V, A184V, N239H, S274T, L324I, V340M, I366V, K434E, E442K, and/or V446I amino acid substitutions. | |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure | |
| Family | ||
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 17/34 |
| Publication No: | US 8603949 B2 |
| Title: | Novel k04-0144 substances and process for production thereof |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | December 10, 2013 |
| Filing Date: | June 15, 2004 |
| Inventors: | Frances H. Arnold, Christopher R. Otey |
| Assignee: | California Institute of Technology CalTech |
| Abstract: | The present disclosure teaches that the recombination of homologous sequences of P450 enzymes, with the aid of SCHEMA to predict a resulting protein structure, is able to generate libraries of chimeras with significant functional diversity. Additionally, the members of these libraries demonstrate superior or unexpected new properties, which correlate with other factors that are observable in the library. Thus, the making of libraries of optimized P450 enzymes, the analysis of libraries to identify an optimized subset, and the optimized chimeras with improved or altered functionalities are all taught in the present disclosure. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 18/34 |
| Publication No: | US 7220563 B2 |
| Title: | Glucose 6-oxidases |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | May 22, 2007 |
| Filing Date: | February 27, 2003 |
| Inventors: | Frances H. Arnold, Lian-Hong Sun, Ioanna P. Petrounia |
| Assignee: | California Institute of Technology CalTech |
| Abstract: | Glucose oxidase enzymes are provided, including novel variants of galactose oxidase enzymes. The polynucleotides that encode these novel variants can be expressed in recombinant host cell expression systems. The novel variant oxidase enzymes are capable of oxidizing compounds towards which wild-type galactose oxidase (e.g. D-galactose: oxygen 6-oxidoreductase, GAO; EC 1.1.3.9) has little or no activity. Preferred galactose oxidase variants are those which that have improved capability to oxidize secondary alcohols and/or D-glucose relative to the wild-type enzyme. |
| Representative Figure: | |
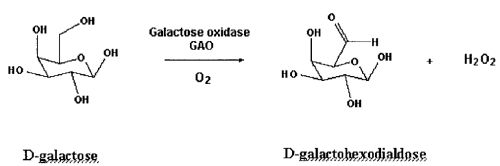 | |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 19/34 |
| Publication No: | US 7214298 B2 |
| Title: | Microfabricated cell sorter |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | May 8, 2007 |
| Filing Date: | August 13, 2001 |
| Inventors: | Charles F. Spence, Anne Y. Fu, Stephen R. Quake, Frances H. Arnold |
| Assignee: | California Institute of Technology CalTech |
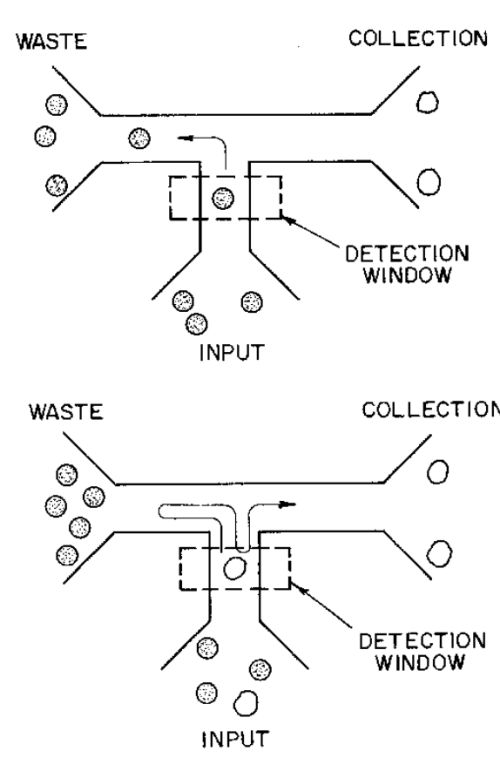
| Abstract: | The invention provides a microfabricated device for sorting cells based on a desired characteristic, for example, reporter-labeled cells can be sorted by the presence or level of reporter on the cells. The device includes a chip having a substrate into which is microfabricated at least one analysis unit. Each analysis unit includes a main channel, having a sample inlet channel, typically at one end, and a detection region along a portion of its length. Adjacent and downstream from the detection region, the main channel has a discrimination region or branch point leading to at least two branch channels. The analysis unit may further include additional inlet channels, detection points, branch points, and branch channels as desired. A stream containing cells is passed through the detection region, such that on average one cell occupies the detection region at a given time. The cells can be sorted into an appropriate branch channel based on the presence or amount of a detectable signal such as an optical signal, with or without stimulation, such as exposure to light in order to promote fluorescence. |
| Representative Figure: | |
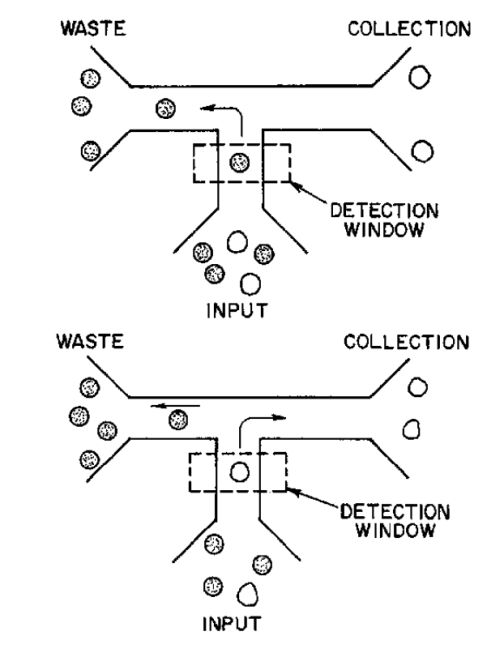 | |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 20/34 |
| Publication No: | AU 755415 B2 |
| Title: | Recombination of polynucleotide sequences using random or defined primers |
| Publication Type: | Australian Patent |
| Publication Date: | February 12, 2002 |
| Filing Date: | December 28, 2000 |
| Inventors: | Joseph A Affholter, Frances H Arnold, Lorraine J. Giver, Zhixin Shao, Huimin Zhao |
| Assignee: | California Institute of Technology CalTech |
| Abstract: | A method for in vitro mutagenesis and recombination of polynucleotide sequences based on polymerase-catalyzed extension of primer oligonucleotides is disclosed. The method involves priming template polynuclcotide(s) with random-sequences or defined-sequence primers to generate a pool of short DNA fragments with a low level of point mutations. Thc DNA fragments are subjected to denaturization followed by annealing and further enzyme-catalyzed DNA polymerization. This procedure is repeated a sufficient number of times to produce full-length genes which comprise mutants of the original template polynucleotides. These genes can be further amplified by the polymerase chain reaction and cloned into a vector for expression of the encoded proteins. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 21/34 |
| Publication No: | US 7098010 B1 |
| Title: | Directed evolution of oxidase enzymes |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | August 29, 2006 |
| Filing Date: | November 27, 2000 |
| Inventors: | Frances H. Arnold, Ioanna P. Petrounia, Lianhong Sun |
| Assignee: | California Institute of Technology CalTech |
| Abstract: | This invention relates to the expression of improved polynucleotide and polypeptide sequences encoding for eukaryotic enzymes, particularly oxidase enzymes. The enzymes are advantagoeusly produced in conventional or facile expression systems. Various methods for directed evolution of polynucleotide sequences can be used to obtain the improved sequences. The improved characteristics of the polypeptides or proteins generated in this manner include improved expression, enhanced activity toward one or more substrates, and increased thermal stability. In a particular embodiment, the invention relates to improved expression of the galactose oxidase gene and galactose oxidase enzymes. GAO mutants that are highly active and/or thermostable are disclosed. |
| Representative Figure: | |
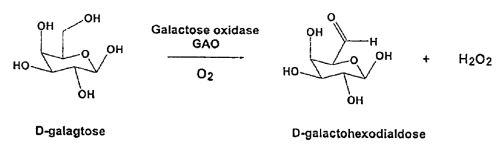 | |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 22/34 |
| Publication No: | US 6361988 B1 |
| Title: | ECB deacylase mutants |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | March 26, 2002 |
| Filing Date: | April 4, 2000 |
| Inventors: | Frances H. Arnold, Zhixin Shao, Huimin Zhao, Lorraine J. Giver |
| Assignee: | California Institute of Technology CalTech |
| Abstract: | A method for in vitro mutagenesis and recombination of polynucleotide sequences based on polymerase-catalyzed extension of primer oligonucleotides is disclosed. The method involves priming template polynucleotide(s) with random-sequences or defined-sequence primers to generate a pool of short DNA fragments with a low level of point mutations. The DNA fragments are subjected to denaturization followed by annealing and further enzyme-catalyzed DNA polymerization. This procedure is repeated a sufficient number of times to produce full-length genes which comprise mutants of the original template polynucleotides. These genes can be further amplified by the polymerase chain reaction and cloned into a vector for expression of the encoded proteins. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 23/34 |
| Publication No: | DE 60020943 D1 |
| Title: | HYDANTOINASE VARIANTS WITH IMPROVED PROPERTIES AND ITS APPLICATION FOR THE PRODUCTION OF AMINO ACIDS |
| Publication Type: | German Patent |
| Publication Date: | July 28, 2005 |
| Filing Date: | March 28, 2000 |
| Inventors: | Frances H Arnold, Oliver May, Karlheinz Drauz, Andreas Bommarius |
| Assignee: | Evonik Operations GmbH, California Institute of Technology CalTech |
| Abstract: | Hydantoinase enzymes which are mutants of a previously isolated hydantoinase having the amino acid SEQ. ID. NO. 2. The mutants include amino acid substitutions at positions 95, 154, 180, 251 and/or 255 of the wild type hydantoinase (SEQ. ID. NO. 2). The mutant hydantoinases, like the parent hydantoinase, are used in the production of optically pure amino acids. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 24/34 |
| Publication No: | US 6177263 B1 |
| Title: | Recombination of polynucleotide sequences using random or defined primers |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | January 23, 2001 |
| Filing Date: | July 14, 1999 |
| Inventors: | Frances H. Arnold, Zhixin Shao, Joseph A. Affholter, Huimin Zhao, Lorraine J. Giver |
| Assignee: | California Institute of Technology CalTech |
| Abstract: | A method for in vitro mutagenesis and recombination of polynucleotide sequences based on polymerase-catalyzed extension of primer oligonucleotides is disclosed. The method involves priming template polynucleotide(s) with random-sequences or defined-sequence primers to generate a pool of short DNA fragments with a low level of point mutations. The DNA fragments are subjected to denaturization followed by annealing and further enzyme-catalyzed DNA polymerization. This procedure is repeated a sufficient number of times to produce full-length genes which comprise mutants of the original template polynucleotides. These genes can be further amplified by the polymerase chain reaction and cloned into a vector for expression of the encoded proteins. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 25/34 |
| Publication No: | US 6540895 B1 |
| Title: | Microfabricated cell sorter for chemical and biological materials |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | April 1, 2003 |
| Filing Date: | May 21, 1999 |
| Inventors: | Charles F. Spence, Anne Y. Fu, Stephen R. Quake, Frances H. Arnold |
| Assignee: | California Institute of Technology CalTech |
| Abstract: | The invention provides a microfabricated device for sorting cells based on a desired characteristic, for example, reporter-labeled cells can be sorted by the presence or level of reporter on the cells. The device includes a chip having a substrate into which is microfabricated at least one analysis unit. Each analysis unit includes a main channel, having a sample inlet channel, typically at one end, and a detection region along a portion of its length. Adjacent and downstream from the detection region, the main channel has a discrimination region or branch point leading to at least two branch channels. The analysis unit may further include additional inlet channels, detection points, branch points, and branch channels as desired. A stream containing cells is passed through the detection region, such that on average one cell occupies the detection region at a given time. The cells can be sorted into an appropriate branch channel based on the presence or amount of a detectable signal such as an optical signal, with or without stimulation, such as exposure to light in order to promote fluorescence. |
| Representative Figure: | |
 | |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 26/34 |
| Publication No: | US 6902918 B1 |
| Title: | Oxygenase enzymes and screening method |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | June 7, 2005 |
| Filing Date: | February 2, 1999 |
| Inventors: | Frances H. Arnold, Hyun Joo, Zhanglin Lin |
| Assignee: | California Institute of Technology CalTech |
| Abstract: | A method for detecting the presence of an oxygenated compound which is produced when a substrate is reacted with an oxygenase for the substrate. The method involves reacting a coupling enzyme with the oxygenated compound to form a polymeric oxygenated compound which is fluorescent or luminescent. Measurement of the fluorescence or luminescence of the polymeric oxygenated compound provides indirect detection of the oxygenated compound produced by reaction of the oxygenase with the substrate. The method is carried out in a whole cell environment wherein the cell is transformed to express both the oxygen a set being screened and the coupling enzyme. The method can be used to measure the activity of monooxygenases and dioxygenases on aromatic substrates. The method is amenable to large scale screening of enzyme mutants to isolate those with maximum oxygenase activity. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 27/34 |
| Publication No: | US 5945325 A |
| Title: | Thermally stable para-nitrobenzyl esterases |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | August 31, 1999 |
| Filing Date: | April 20, 1998 |
| Inventors: | Frances H. Arnold, Lorraine J. Giver |
| Assignee: | California Institute of Technology CalTech |
| Abstract: | A method for isolating and identifying modified para-nitrobenzyl esterases which exhibit improved thermal stability relative to naturally occurring para-nitrobenzyl esterase. The method involves preparing a library of modified para-nitrobenzyl esterase nucleic acid segments (genes) which have nucleotide sequences that differ from the nucleic acid segment which encodes for naturally occurring para-nitrobenzyl esterase. The library of modified para-nitrobenzyl nucleic acid segments is expressed to provide a plurality of modified enzymes. The clones expressing modified enzymes are then screened to identify which enzymes retain esterase activity after heat treatment at elevated temperature. Specific modified para-nitrobenzyl esterases are disclosed which have improved thermal stability and/or ester hydrolysis activity in aqueous or aqueous-organic media relative to the thermal stability and/or ester hydrolysis activity of unmodified naturally occurring para-nitrobenzyl esterase |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 28/34 |
| Publication No: | US 5906930 A |
| Title: | Para-nitrobenzyl esterases with enhanced activity in aqueous and nonaqueous media |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | May 25, 1999 |
| Filing Date: | February 9, 1998 |
| Inventors: | Frances H. Arnold, Jeffrey C. Moore |
| Assignee: | California Institute of Technology CalTech |
| Abstract: | A method for isolating and identifying modified para-nitrobenzyl esterases which exhibit improved stability and/or esterase hydrolysis activity toward selected substrates and under selected reaction conditions relative to the unmodified para-nitrobenzyl esterase. The method involves preparing a library of modified para-nitrobenzyl esterase nucleic acid segments (genes) which have nucleotide sequences that differ from the nucleic acid segment which encodes for unmodified para-nitrobenzyl esterase. The library of modified para-nitrobenzyl nucleic acid segments is expressed to provide a plurality of modified enzymes. The clones expressing modified enzymes are then screened to identify which enzymes have improved esterase activity by measuring the ability of the enzymes to hydrolyze the selected substrate under the selected reaction conditions. Specific modified para-nitrobenzyl esterases are disclosed which have improved stability and/or ester hydrolysis activity in aqueous or aqueous-organic media relative to the stability and/or ester hydrolysis activity of unmodified naturally occurring para-nitrobenzyl esterase. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 29/34 |
| Publication No: | US 6063637 A |
| Title: | Sensors for sugars and other metal binding analytes |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | May 16, 2000 |
| Filing Date: | March 3, 1997 |
| Inventors: | Frances H. Arnold, Zhibin Guan, Chao-Tsen Chen, Guohua Chen |
| Assignee: | California Institute of Technology CalTech |
| Abstract: | Sensors (20, 50, 70) for use in detecting the presence of sugars and other analytes (target molecules). The sensor is composed of a metal complex that binds to the target molecule and releases a proton or includes an exchangable ligand which is exchanged for the target molecule during the binding interaction between the metal complex and the target molecule. The result of the binding interaction is the release of a proton, hydroxide ion or ligand species generated during the ligand exchange. Measurement of the release of proton, hydroxide ion or other ligand species from the sensor (20, 50, 70) provides an indirect indication of target molecule concentration. The metal complexes may be attached to support structures (10, 12) to provide both anchoring and positioning of the metal ions to increase selectivity of sugar/metal complex interactions. Detection systems in which pH is used as an indication of proton or hydroxide release are disclosed, as are detection systems in which Cl- release is used. Methods for monitoring the concentrations of sugars and related molecules using the metal based sensors (20, 50, 70) are also disclosed. |
| Representative Figure: | |
 | |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 30/34 |
| Publication No: | US 5837202 A |
| Title: | Metal chelating lipids which are useful as sensors in fluorometric methods for the detection of metal ions |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | November 17, 1998 |
| Filing Date: | September 11, 1996 |
| Inventors: | Frances H. Arnold, Darryl Y. Sasaki |
| Assignee: | California Institute of Technology CalTech |
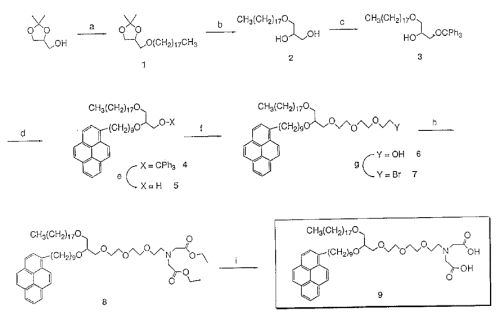
| Abstract: | A fluorescent metal-chelating amphiphile having the structure: ##STR1## wherein A is a hydrophobic fluorophore, X and Y are aliphatic hydrocarbons having from 9 to 25 carbon atoms, B is a hydrophilic spacer, C is a metal chelator, and L is either an ether or ester linkage. The fluorescent metal-chelating amphiphile is combined with a matrix lipid to form lipid-based sensors which provide fluorometric detection of metal ions in liquids. |
| Representative Figure: | |
 | |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 31/34 |
| Publication No: | US 5786428 A |
| Title: | Adsorbents for amino acid and peptide separation |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | July 28, 1998 |
| Filing Date: | March 27, 1996 |
| Inventors: | Frances H. Arnold, Vidyasankar Sundaresan |
| Assignee: | California Institute of Technology CalTech |
| Abstract: | An adsorbent which selectively binds to one enantiomer of an optically active amino acid or peptide. The adsorbent includes a polymer matrix which contains one or more metal complexes that are oriented within the polymer matrix by molecular imprinting to provide selective binding of the matrix to only one enantiomer of the optically active amino acid or peptide. Separation systems are disclosed which use the adsorbent as the basis for conducting enantioresolution of optically active amino acids and peptides. Methods for using the adsorbent are also disclosed. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 32/34 |
| Publication No: | US 5283339 A |
| Title: | Immobilized metal aqueous two-phase extraction and precipitation |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | February 1, 1994 |
| Filing Date: | August 5, 1992 |
| Inventors: | Frances H. Arnold, Gerald E. Wuenschell |
| Assignee: | California Institute of Technology CalTech |
| Abstract: | Metallated compounds can be used to extract or precipitate proteins from solution. The compounds can be polymers, such as polyalkylene glycols, which can be mono- or bimetallated or smaller bis-metal chelates, such as ethylenebis(oxyethylenenitrilo)tetraacetic acid. The monometallated polymers are preferred in the extraction process whereas the bimetallated compounds are preferred in the precipitation process. In addition, new PEG compounds which are capable of chelating a variety of metals are described. Both mono- and bi-metallated forms are set forth. The new metallated compounds are very effective in extracting or precipitating proteins from solution. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 33/34 |
| Publication No: | US 5316935 A |
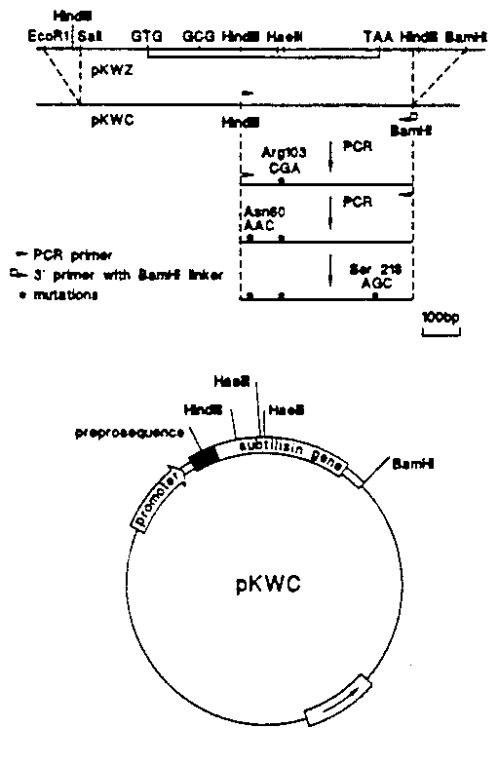
| Title: | Subtilisin variants suitable for hydrolysis and synthesis in organic media |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | May 31, 1994 |
| Filing Date: | April 6, 1992 |
| Inventors: | Frances H. Arnold, Keqin Chen |
| Assignee: | California Institute of Technology CalTech |
| Abstract: | In accordance with the present invention, there are provided novel, modified subtilisin enzyme(s) having improved catalytic activity and/or stability in organic media. |
| Representative Figure: | |
 | |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 34/34 |
| Publication No: | US 5310648 A |
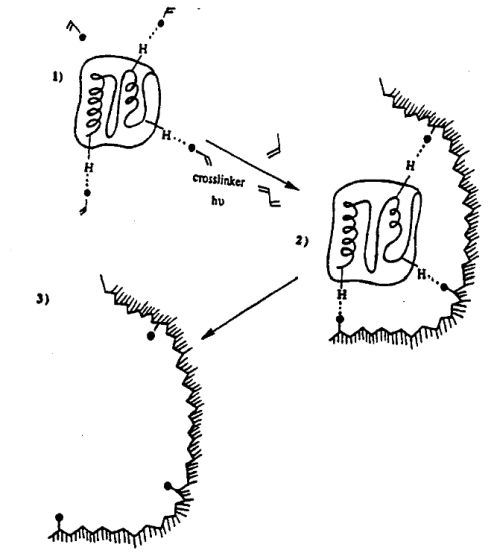
| Title: | Composition of matter comprising an imprinted matrix exhibiting selective binding interactions through chelated metals |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | May 10, 1994 |
| Filing Date: | February 1, 1991 |
| Inventors: | Frances H. Arnold, Pradeep Dhal, Deborah Shnek, Sean Plunkett |
| Assignee: | California Institute of Technology CalTech |
| Abstract: | The invention provides an imprinted matrix which exhibits selective binding interactions through metal chelates with a predetermined molecule or biological particle. Also provided is a preformed, fluid-imprinted matrix having sufficient rigidity to maintain selective binding interaction with a predetermined molecule or biological particle through interactive moieties. Methods for producing such matrices are additionally provided. |
| Representative Figure: | |
 | |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
Discover Your Abilities and Aspirations!
 $10 $25 $50 $100 Other
$10 $25 $50 $100 Other
Tax Exempt 501(c)3 Non-Profit Organization
Any Currency
“One comes to be of just such stuff as that on which the mind is set” - Maithri Upanishath, VI.34:3
“…the peace that is found in libraries and laboratories…” - Louis Pasteur
“…the peace that is found in libraries and laboratories…” - Louis Pasteur
Contact Us E-Mail: info@GangaLib.org
Ganga library non-profit 501(c)(3) org. Contributions tax deductible. IRS Tax ID 46-2892728
Copyright © 2023 Ganga Library Inc. All Rights reserved.;
Copyright © 2023 Ganga Library Inc. All Rights reserved.;

Painting Tim Tompkins - PaintHistory.com
Name: Frances H. Arnold
Birth: 25 July 1956, Pittsburgh, PA, USA
Institution: California Institute of Technology (Caltech), Pasadena, CA, USA
Award: "for the directed evolution of enzymes."
Portion of Cash: 1/3
Patents